Main Model Class
The main TV Transmitter model class, TvSpectrumTransmitter, provides a
user-configurable PSD model that can be transmitted on the SpectrumChannel.
It inherits from SpectrumPhy and is comprised of attributes and methods to
create and transmit the signal on the channel.
One of the user-configurable attributes is the type of modulation for the TV
transmitter to use. The options are 8-VSB (Eight-Level Vestigial Sideband
Modulation) which is notably used in the North America ATSC digital television
standard, COFDM (Coded Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) which is
notably used in the DVB-T and ISDB-T digital television standards adopted by
various countries around the world, and analog modulation which is a legacy
technology but is still being used by some countries today. To accomplish
realistic PSD models for these modulation types, the signals’ PSDs were
approximated from real standards and developed into models that are scalable by
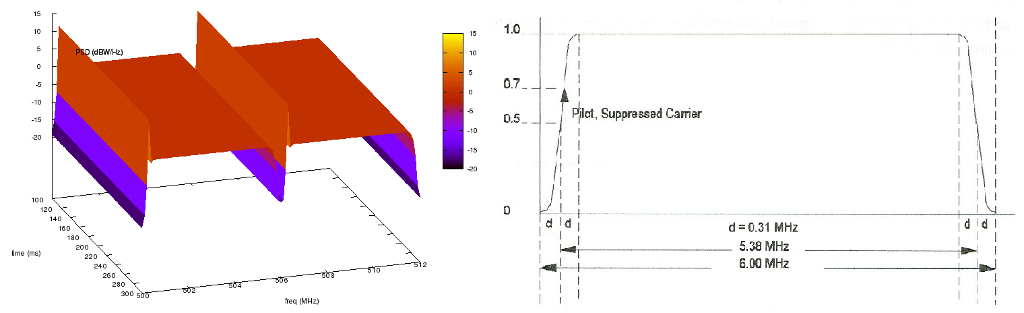
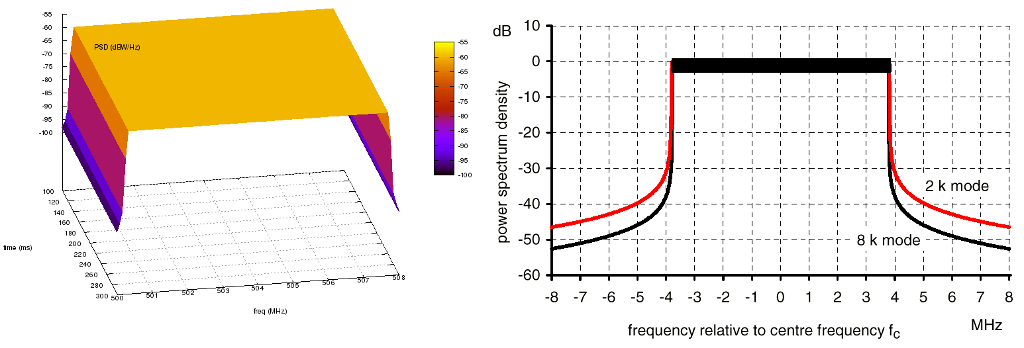
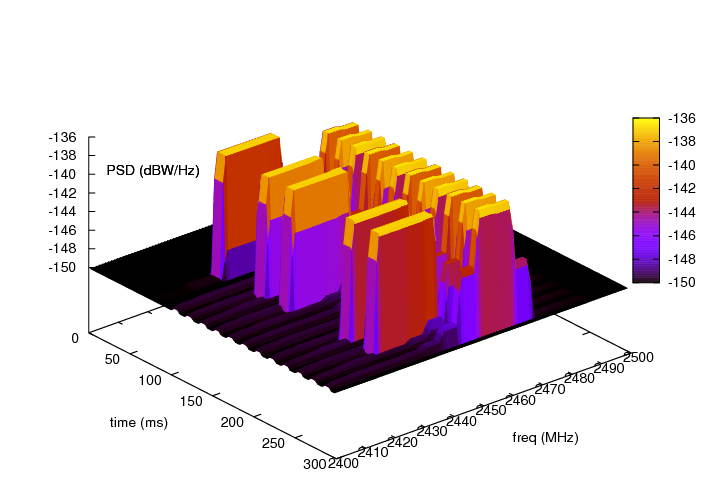
frequency and power. The COFDM PSD is approximated from Figure 12 (8k mode) of
[KoppCOFDM], the 8-VSB PSD is approximated from Figure 3 of [Baron8VSB], and the
analog PSD is approximated from Figure 4 of [QualcommAnalog]. Note that the
analog model is approximated from the NTSC standard, but other analog modulation
standards such as PAL have similar signals. The approximated COFDM PSD model is
in 8K mode. The other configurable attributes are the start frequency,
signal/channel bandwidth, base PSD, antenna type, starting time,
and transmit duration.
TvSpectrumTransmitter uses IsotropicAntennaModel as its antenna model by
default, but any model that inherits from AntennaModel is selectable, so
directional antenna models can also be used. The propagation loss models used
in simulation are configured in the SpectrumChannel that the user chooses to
use. Terrain and spherical Earth/horizon effects may be supported in future ns-3
propagation loss models.
After the attributes are set, along with the SpectrumChannel,
MobilityModel, and node locations, the PSD of the TV transmitter signal can
be created and transmitted on the channel.
Helper Class
The helper class, TvSpectrumTransmitterHelper, consists of features to
assist users in setting up TV transmitters for their simulations. Functionality
is also provided to easily simulate real-world scenarios.
Using this helper class, users can easily set up TV transmitters right after
configuring attributes. Multiple transmitters can be created at a time. Also
included are real characteristics of specific geographic regions that can be
used to run realistic simulations. The regions currently included are
North America, Europe, and Japan. The frequencies and bandwidth of each TV
channel for each these regions are provided.
A method (CreateRegionalTvTransmitters) is provided that enables users to
randomly generate multiple TV transmitters from a specified region with a given
density within a chosen radius around a point on Earth’s surface. The region,
which determines the channel frequencies of the generated TV transmitters, can
be specified to be one of the three provided, while the density determines the
amount of transmitters generated. The TV transmitters’ antenna heights
(altitude) above Earth’s surface can also be randomly generated to be within a
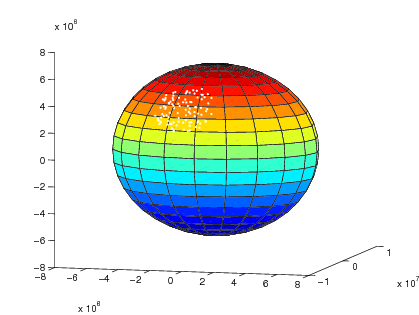
given maximum altitude. This method models Earth as a perfect sphere, and
generated location points are referenced accordingly in Earth-Centered
Earth-Fixed Cartesian coordinates. Note that bodies of water on Earth are not
considered in location point generation–TV transmitters can be generated
anywhere on Earth around the origin point within the chosen maximum radius.
Testing
The tv-spectrum-transmitter test suite verifies the accuracy of the
spectrum/PSD model in TvSpectrumTransmitter by testing if the maximum power
spectral density, start frequency, and end frequency comply with expected values
for various test cases.
The tv-helper-distribution test suite verifies the functionality of the
method in TvSpectrumTransmitterHelper that generates a random number of TV
transmitters based on the given density (low, medium, or high) and maximum
number of TV channels. It verifies that the number of TV transmitters generated
does not exceed the expected bounds.
The CreateRegionalTvTransmitters method in TvSpectrumTransmitterHelper
described in Helper Class uses two methods from the
GeographicPositions class in the Mobility module to generate the random
Cartesian points on or above earth’s surface around an origin point which
correspond to TV transmitter positions. The first method converts Earth
geographic coordinates to Earth-Centered Earth-Fixed (ECEF) Cartesian
coordinates, and is tested in the geo-to-cartesian test suite by comparing
(with 10 meter tolerance) its output with the output of the geographic to ECEF
conversion function [MatlabGeo] of the MATLAB Mapping Toolbox for numerous
test cases. The other used method generates random ECEF Cartesian points around
the given geographic origin point, and is tested in the rand-cart-around-geo
test suite by verifying that the generated points do not exceed the given
maximum distance radius from the origin point.
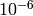 which is to account for
numerical errors.
which is to account for
numerical errors.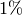 of the PHY rate;
of the PHY rate;