A Device for a Csma Network Link. More...
#include <csma-net-device.h>
Public Types | |
| enum | EncapsulationMode { ILLEGAL, DIX, LLC } |
Public Member Functions | |
| CsmaNetDevice () | |
| virtual | ~CsmaNetDevice () |
| void | SetInterframeGap (Time t) |
| void | SetBackoffParams (Time slotTime, uint32_t minSlots, uint32_t maxSlots, uint32_t maxRetries, uint32_t ceiling) |
| bool | Attach (Ptr< CsmaChannel > ch) |
| void | SetQueue (Ptr< Queue > queue) |
| void | SetReceiveErrorModel (Ptr< ErrorModel > em) |
| void | Receive (Ptr< Packet > p, Ptr< CsmaNetDevice > sender) |
| bool | IsSendEnabled (void) |
| void | SetSendEnable (bool enable) |
| bool | IsReceiveEnabled (void) |
| void | SetReceiveEnable (bool enable) |
| void | SetAddress (Mac48Address addr) |
| void | SetFrameSize (uint16_t frameSize) |
| uint16_t | GetFrameSize (void) const |
| void | SetEncapsulationMode (CsmaNetDevice::EncapsulationMode mode) |
| CsmaNetDevice::EncapsulationMode | GetEncapsulationMode (void) |
| virtual void | SetName (const std::string name) |
| virtual std::string | GetName (void) const |
| virtual void | SetIfIndex (const uint32_t index) |
| virtual uint32_t | GetIfIndex (void) const |
| virtual Ptr< Channel > | GetChannel (void) const |
| virtual bool | SetMtu (const uint16_t mtu) |
| virtual uint16_t | GetMtu (void) const |
| virtual Address | GetAddress (void) const |
| virtual bool | IsLinkUp (void) const |
| virtual void | SetLinkChangeCallback (Callback< void > callback) |
| virtual bool | IsBroadcast (void) const |
| virtual Address | GetBroadcast (void) const |
| virtual bool | IsMulticast (void) const |
| virtual Address | GetMulticast (Ipv4Address multicastGroup) const |
| Make and return a MAC multicast address using the provided multicast group. | |
| virtual bool | IsPointToPoint (void) const |
| virtual bool | IsBridge (void) const |
| virtual bool | Send (Ptr< Packet > packet, const Address &dest, uint16_t protocolNumber) |
| virtual bool | SendFrom (Ptr< Packet > packet, const Address &source, const Address &dest, uint16_t protocolNumber) |
| virtual Ptr< Node > | GetNode (void) const |
| virtual void | SetNode (Ptr< Node > node) |
| virtual bool | NeedsArp (void) const |
| virtual void | SetReceiveCallback (NetDevice::ReceiveCallback cb) |
| virtual Address | GetMulticast (Ipv6Address addr) const |
| Get the MAC multicast address corresponding to the IPv6 address provided. | |
| virtual void | SetPromiscReceiveCallback (PromiscReceiveCallback cb) |
| virtual bool | SupportsSendFrom (void) const |
Static Public Member Functions | |
| static TypeId | GetTypeId (void) |
| This method returns the TypeId associated to ns3::CsmaNetDevice. | |
Protected Member Functions | |
| virtual void | DoDispose (void) |
| Ptr< Queue > | GetQueue (void) const |
| void | AddHeader (Ptr< Packet > p, Mac48Address source, Mac48Address dest, uint16_t protocolNumber) |
| bool | ProcessHeader (Ptr< Packet > p, uint16_t ¶m) |
Private Types | |
| enum | TxMachineState { READY, BUSY, GAP, BACKOFF } |
Private Member Functions | |
| CsmaNetDevice & | operator= (const CsmaNetDevice &o) |
| CsmaNetDevice (const CsmaNetDevice &o) | |
| void | Init (bool sendEnable, bool receiveEnable) |
| uint32_t | MtuFromFrameSize (uint32_t frameSize) |
| uint32_t | FrameSizeFromMtu (uint32_t mtu) |
| void | TransmitStart () |
| void | TransmitCompleteEvent (void) |
| void | TransmitReadyEvent (void) |
| void | TransmitAbort (void) |
| void | NotifyLinkUp (void) |
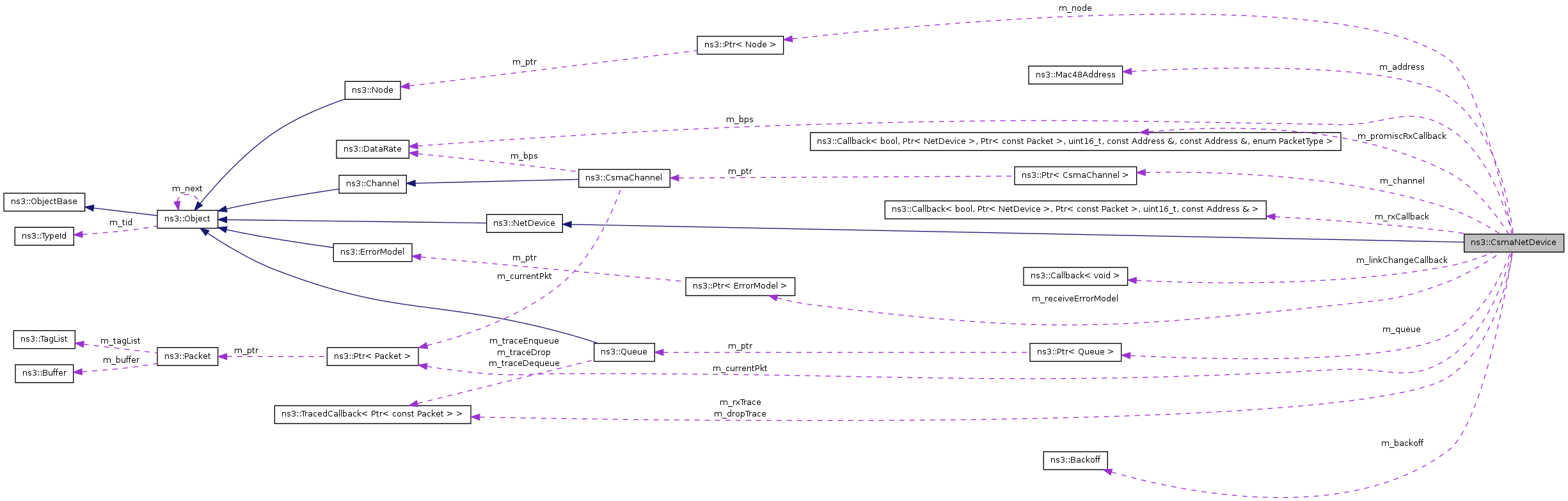
Private Attributes | |
| uint32_t | m_deviceId |
| bool | m_sendEnable |
| bool | m_receiveEnable |
| TxMachineState | m_txMachineState |
| EncapsulationMode | m_encapMode |
| DataRate | m_bps |
| Time | m_tInterframeGap |
| Backoff | m_backoff |
| Ptr< Packet > | m_currentPkt |
| Ptr< CsmaChannel > | m_channel |
| Ptr< Queue > | m_queue |
| Ptr< ErrorModel > | m_receiveErrorModel |
| TracedCallback< Ptr< const Packet > > | m_rxTrace |
| TracedCallback< Ptr< const Packet > > | m_dropTrace |
| Ptr< Node > | m_node |
| Mac48Address | m_address |
| NetDevice::ReceiveCallback | m_rxCallback |
| NetDevice::PromiscReceiveCallback | m_promiscRxCallback |
| uint32_t | m_ifIndex |
| std::string | m_name |
| bool | m_linkUp |
| Callback< void > | m_linkChangeCallback |
| uint32_t | m_frameSize |
| uint32_t | m_mtu |
Detailed Description
A Device for a Csma Network Link.
The Csma net device class is analogous to layer 1 and 2 of the TCP stack. The NetDevice takes a raw packet of bytes and creates a protocol specific packet from them.
Each Csma net device will receive all packets written to the Csma link. The ProcessHeader function can be used to filter out the packets such that higher level layers only receive packets that are addressed to their associated net devices
Member Enumeration Documentation
Enumeration of the types of packets supported in the class.
- Enumerator:
ILLEGAL Encapsulation mode not set
DIX DIX II / Ethernet II packet
LLC 802.2 LLC/SNAP Packet
enum ns3::CsmaNetDevice::TxMachineState [private] |
Enumeration of the states of the transmit machine of the net device.
Constructor & Destructor Documentation
| ns3::CsmaNetDevice::CsmaNetDevice | ( | ) |
Construct a CsmaNetDevice
This is the default constructor for a CsmaNetDevice.
| virtual ns3::CsmaNetDevice::~CsmaNetDevice | ( | ) | [virtual] |
Destroy a CsmaNetDevice
This is the destructor for a CsmaNetDevice.
| ns3::CsmaNetDevice::CsmaNetDevice | ( | const CsmaNetDevice & | o | ) | [private] |
Copy constructor is declared but not implemented. This disables the copy constructor for CsmaNetDevice objects.
Member Function Documentation
| void ns3::CsmaNetDevice::AddHeader | ( | Ptr< Packet > | p, | |
| Mac48Address | source, | |||
| Mac48Address | dest, | |||
| uint16_t | protocolNumber | |||
| ) | [protected] |
Adds the necessary headers and trailers to a packet of data in order to respect the packet type
- Parameters:
-
p Packet to which header should be added source MAC source address from which packet should be sent dest MAC destination address to which packet should be sent protocolNumber In some protocols, identifies the type of payload contained in this packet.
| bool ns3::CsmaNetDevice::Attach | ( | Ptr< CsmaChannel > | ch | ) |
Attach the device to a channel.
The function Attach is used to add a CsmaNetDevice to a CsmaChannel.
- See also:
- SetDataRate ()
- SetInterframeGap ()
- Parameters:
-
ch a pointer to the channel to which this object is being attached.
| virtual void ns3::CsmaNetDevice::DoDispose | ( | void | ) | [protected, virtual] |
Perform any object release functionality required to break reference cycles in reference counted objects held by the device.
Reimplemented from ns3::Object.
| uint32_t ns3::CsmaNetDevice::FrameSizeFromMtu | ( | uint32_t | mtu | ) | [private] |
Calculate the value for the frame size that would be required to be able to set the MTU to the given value.
| virtual Address ns3::CsmaNetDevice::GetAddress | ( | void | ) | const [virtual] |
- Returns:
- the current Address of this interface.
Implements ns3::NetDevice.
| virtual Address ns3::CsmaNetDevice::GetBroadcast | ( | void | ) | const [virtual] |
- Returns:
- the broadcast address supported by this netdevice.
Calling this method is invalid if IsBroadcast returns not true.
Implements ns3::NetDevice.
- Returns:
- the channel this NetDevice is connected to. The value returned can be zero if the NetDevice is not yet connected to any channel.
Implements ns3::NetDevice.
| CsmaNetDevice::EncapsulationMode ns3::CsmaNetDevice::GetEncapsulationMode | ( | void | ) |
Get the encapsulation mode of this device.
- Returns:
- The encapsulation mode of this device.
| uint16_t ns3::CsmaNetDevice::GetFrameSize | ( | void | ) | const |
Get The max frame size of packets sent over this device.
- Returns:
- The max frame size of packets sent over this device.
| virtual uint32_t ns3::CsmaNetDevice::GetIfIndex | ( | void | ) | const [virtual] |
- Returns:
- index ifIndex of the device
Implements ns3::NetDevice.
| virtual uint16_t ns3::CsmaNetDevice::GetMtu | ( | void | ) | const [virtual] |
- Returns:
- the link-level MTU in bytes for this interface.
This value is typically used by the IP layer to perform IP fragmentation when needed.
Implements ns3::NetDevice.
| virtual Address ns3::CsmaNetDevice::GetMulticast | ( | Ipv6Address | addr | ) | const [virtual] |
Get the MAC multicast address corresponding to the IPv6 address provided.
- Parameters:
-
addr IPv6 address
- Returns:
- the MAC multicast address
- Warning:
- Calling this method is invalid if IsMulticast returns not true.
Implements ns3::NetDevice.
| virtual Address ns3::CsmaNetDevice::GetMulticast | ( | Ipv4Address | multicastGroup | ) | const [virtual] |
Make and return a MAC multicast address using the provided multicast group.
RFC 1112 says that an Ipv4 host group address is mapped to an Ethernet multicast address by placing the low-order 23-bits of the IP address into the low-order 23 bits of the Ethernet multicast address 01-00-5E-00-00-00 (hex).
This method performs the multicast address creation function appropriate to an EUI-48-based CSMA device. This MAC address is encapsulated in an abstract Address to avoid dependencies on the exact address format.
- Parameters:
-
multicastGroup The IP address for the multicast group destination of the packet.
- Returns:
- The MAC multicast Address used to send packets to the provided multicast group.
- See also:
- Ipv4Address
- Mac48Address
- Address
Implements ns3::NetDevice.
| virtual std::string ns3::CsmaNetDevice::GetName | ( | void | ) | const [virtual] |
- Returns:
- name name of the device (e.g. "eth0")
Implements ns3::NetDevice.
Get the node to which this device is attached.
Implements ns3::NetDevice.
Get a copy of the attached Queue.
This method is provided for any derived class that may need to get direct access to the underlying queue.
- Returns:
- a pointer to the queue.
| static TypeId ns3::CsmaNetDevice::GetTypeId | ( | void | ) | [static] |
This method returns the TypeId associated to ns3::CsmaNetDevice.
This object is accessible through the following paths with Config::Set and Config::Connect:
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3CsmaNetDevice
Attributes defined for this type:
-
Address: The MAC address of this device.
- Set with class: Mac48AddressValue
- Underlying type: Mac48Address
- Initial value: ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
- Flags: construct write read
-
FrameSize: The maximum size of a packet sent over this device.
- Set with class: ns3::UintegerValue
- Underlying type: uint16_t 0:65535
- Initial value: 1518
- Flags: construct write read
-
EncapsulationMode: The link-layer encapsulation type to use.
- Set with class: ns3::EnumValue
- Underlying type: Dix|Llc
- Initial value: Dix
- Flags: construct write
-
SendEnable: Enable or disable the transmitter section of the device.
- Set with class: BooleanValue
- Underlying type: bool
- Initial value: true
- Flags: construct write read
-
ReceiveEnable: Enable or disable the receiver section of the device.
- Set with class: BooleanValue
- Underlying type: bool
- Initial value: true
- Flags: construct write read
-
ReceiveErrorModel: The receiver error model used to simulate packet loss
- Set with class: ns3::PointerValue
- Underlying type: ns3::Ptr< ns3::ErrorModel >
- Initial value: 0
- Flags: construct write read
-
TxQueue: A queue to use as the transmit queue in the device.
- Set with class: ns3::PointerValue
- Underlying type: ns3::Ptr< ns3::Queue >
- Initial value: 0
- Flags: construct write read
Attributes defined in parent class ns3::NetDevice:
-
Mtu: The MAC-level Maximum Transmission Unit
- Set with class: ns3::UintegerValue
- Underlying type: uint16_t 0:65535
- Flags: write read
TraceSources defined for this type:
- Rx: Trace source indicating reception of packet destined for broadcast, multicast or local address.
- Drop: Trace source indicating packet discarded due to receiver disabled or error model decision.
Reimplemented from ns3::NetDevice.
| void ns3::CsmaNetDevice::Init | ( | bool | sendEnable, | |
| bool | receiveEnable | |||
| ) | [private] |
Initialization function used during object construction.
| virtual bool ns3::CsmaNetDevice::IsBridge | ( | void | ) | const [virtual] |
| virtual bool ns3::CsmaNetDevice::IsBroadcast | ( | void | ) | const [virtual] |
- Returns:
- true if this interface supports a broadcast address, false otherwise.
Implements ns3::NetDevice.
| virtual bool ns3::CsmaNetDevice::IsLinkUp | ( | void | ) | const [virtual] |
- Returns:
- true if link is up; false otherwise
Implements ns3::NetDevice.
| virtual bool ns3::CsmaNetDevice::IsMulticast | ( | void | ) | const [virtual] |
- Returns:
- value of m_isMulticast flag
Implements ns3::NetDevice.
| virtual bool ns3::CsmaNetDevice::IsPointToPoint | ( | void | ) | const [virtual] |
| bool ns3::CsmaNetDevice::IsReceiveEnabled | ( | void | ) |
Is the receive side of the network device enabled?
- Returns:
- True if the receiver side is enabled, otherwise false.
| bool ns3::CsmaNetDevice::IsSendEnabled | ( | void | ) |
Is the send side of the network device enabled?
- Returns:
- True if the send side is enabled, otherwise false.
| uint32_t ns3::CsmaNetDevice::MtuFromFrameSize | ( | uint32_t | frameSize | ) | [private] |
Calculate the value for the MTU that would result from setting the frame size to the given value.
| virtual bool ns3::CsmaNetDevice::NeedsArp | ( | void | ) | const [virtual] |
Does this device need to use the address resolution protocol?
- Returns:
- True if the encapsulation mode is set to a value that requires ARP (IP_ARP or LLC).
Implements ns3::NetDevice.
| void ns3::CsmaNetDevice::NotifyLinkUp | ( | void | ) | [private] |
Notify any interested parties that the link has come up.
| CsmaNetDevice& ns3::CsmaNetDevice::operator= | ( | const CsmaNetDevice & | o | ) | [private] |
Operator = is declared but not implemented. This disables the assigment operator for CsmaNetDevice objects.
Removes, from a packet of data, all headers and trailers that relate to the packet type
- Parameters:
-
p Packet whose headers need to be processed param An integer parameter that can be set by the function to return information gathered in the header
- Returns:
- Returns true if the packet should be forwarded up the protocol stack.
| void ns3::CsmaNetDevice::Receive | ( | Ptr< Packet > | p, | |
| Ptr< CsmaNetDevice > | sender | |||
| ) |
Receive a packet from a connected CsmaChannel.
The CsmaNetDevice receives packets from its connected channel and forwards them up the protocol stack. This is the public method used by the channel to indicate that the last bit of a packet has arrived at the device.
- See also:
- CsmaChannel
- Parameters:
-
p a reference to the received packet sender the CsmaNetDevice that transmitted the packet in the first place
| virtual bool ns3::CsmaNetDevice::Send | ( | Ptr< Packet > | packet, | |
| const Address & | dest, | |||
| uint16_t | protocolNumber | |||
| ) | [virtual] |
Start sending a packet down the channel.
Implements ns3::NetDevice.
| virtual bool ns3::CsmaNetDevice::SendFrom | ( | Ptr< Packet > | packet, | |
| const Address & | source, | |||
| const Address & | dest, | |||
| uint16_t | protocolNumber | |||
| ) | [virtual] |
Start sending a packet down the channel, with MAC spoofing
Implements ns3::NetDevice.
| void ns3::CsmaNetDevice::SetAddress | ( | Mac48Address | addr | ) |
Set the MAC address of the the network device.
- Parameters:
-
addr The Mac48Address to use as the address of the device.
| void ns3::CsmaNetDevice::SetBackoffParams | ( | Time | slotTime, | |
| uint32_t | minSlots, | |||
| uint32_t | maxSlots, | |||
| uint32_t | maxRetries, | |||
| uint32_t | ceiling | |||
| ) |
Set the backoff parameters used to determine the wait to retry transmitting a packet when the channel is busy.
- See also:
- Attach ()
- Parameters:
-
slotTime Length of a packet slot (or average packet time) minSlots Minimum number of slots to wait maxSlots Maximum number of slots to wait maxRetries Maximum number of retries before packet is discard ceiling Cap on the exponential function when calculating max slots
| void ns3::CsmaNetDevice::SetEncapsulationMode | ( | CsmaNetDevice::EncapsulationMode | mode | ) |
Set the encapsulation mode of this device.
- Parameters:
-
mode The encapsulation mode of this device.
- See also:
- SetFrameSize
| void ns3::CsmaNetDevice::SetFrameSize | ( | uint16_t | frameSize | ) |
Set The max frame size of packets sent over this device.
Okay, that was easy to say, but the details are a bit thorny. We have a MAC-level MTU that is the payload that higher level protocols see. We have a PHY-level MTU which is the maximum number of bytes we can send over the link (cf. 1500 bytes for Ethernet). We also have a frame size which is some total number of bytes in a packet which could or could not include any framing and overhead. There can be a lot of inconsistency in definitions of these terms. For example, RFC 1042 asserts that the terms maximum transmission unit and maximum packet size are equivalent. RFC 791, however, defines MTU as the maximum sized IP datagram that can be sent. Packet size and frame size are sometimes used interchangeably.
So, some careful definitions are in order to avoid confusion:
In real Ethernet, a packet on the wire starts with a preamble of seven bytes of alternating ones and zeroes followed by a Start-of-Frame-Delimeter (10101011). This is followed by what is usually called the packet: a MAC destination and source, a type field, payload, a possible padding field and a CRC. To be strictly and pedantically correct the frame size is necessarily larger than the packet size on a real Ethernet. But, this isn't a real Ethernet, it's a simulation of a device similar to Ethernet, and we have no good reason to add framing bits. So, in the case of the CSMA device, the frame size is equal to the packet size. Since these two values are equal, there is no danger in assuming they are identical. We do not implement any padding out to a minimum frame size, so padding is a non-issue. We define packet size to be equal to frame size and this excludes the preamble and SFD bytes of a real Ethernet frame. We define a single (MAC-level) MTU that coresponds to the payload size of the packet, which is the IP-centric view of the term as seen in RFC 791.
To make this concrete, consider DIX II (Digital Equipment, Intel, Xerox type II) framing, which is used in most TCP/IP stacks. NetWare and Wireshark call this framing Ethernet II, by the way. In this framing scheme, a real packet on the wire starts with the preamble and Start-of-Frame-Delimeter (10101011). We ignore these bits on this device since it they are not needed. In DIX II, the SFD is followed by the MAC (48) destination address (6 bytes), source address (6 bytes), the EtherType field (2 bytes), payload (0-1500 bytes) and a CRC (4 bytes) -- this corresponds to our entire frame. The payload of the packet/frame in DIX can be from 0 to 1500 bytes. It is the maxmimum value of this payload that we call the MTU. Typically, one sees the MTU set to 1500 bytes and the maximum frame size set to 1518 bytes in Ethernet-based networks.
Different framing schemes can make for different MTU and frame size relationships. For example, we support LLC/SNAP encapsulation which adds eight bytes of header overhead to the usual DIX framing. In this case, if the maximum frame size is left at 1518 bytes, we need to export an MTU that reflects the loss of eight bytes for a total of 1492.
Another complication is that IEEE 802.1Q adds four bytes to the maximum frame size for VLAN tagging. In order to provide an MTU of 1500 bytes, the frame size would need to increased to 1522 bytes to absorb the additional overhead.
So, there are really three variables that are not entirely free at work here. There is the maximum frame size, the MTU and the framing scheme which we call the encapsulation mode.
So, what do we do since there are be three values which must always be consistent in the driver? Which values to we allow to be changed and how do we ensure the other two are consistent? We want to actually allow a user to change these three variables in flexible ways, but we want the results (even at intermediate stages of her ultimate change) to be consistent. We certainly don't want to require that users must understand the various requirements of an enapsulation mode in order to set these variables.
Consider the following situation: A user wants to set the maximum frame size to 1418 bytes instead of 1518. This user shouldn't have to concern herself that the current encapuslation mode is LLC/SNAP and this will consume eight bytes. She should not have to also figure out that the MTU needs to be set to 1392 bytes, and she should certainly not have to do this in some special order to keep intermediate steps consistent.
Similarly, a user who is interested in setting the MTU to 1400 bytes should not be forced to understand that (based on encapsulation mode) the frame size may need to be set to eighteen + eight bytes more than what he wants in certain cases (802,3 + LLC/SNAP), twenty-two + zero bytes in others (802.1Q) and other inscrutable combinations
Now, consider a user who is only interested in changing the encapsulation mode from LLC/SNAP to DIX. This is going to change the relationship between the MTU and the frame size. We've may have to come up with a new value for at least one of the these? Which one? There are too many free variables.
We could play games trying to figure out what the user wants to do, but that is typically a bad plan and programmers have a long and distinguished history of guessing wrong. We'll avoid all of that and just define a flexible behavior that can be worked to get what you want. Here it is:
- If the user is changing the encapsulation mode, the PHY MTU will remain fixed and the MAC MTU will change, if required, to make the three values consistent;
- If the user is changing the MTU, she is interested in getting that part of the system set, so the frame size will be changed to make the three values consistent;
- If the user is changing the frame size, he is interested in getting that part of the system set, so the MTU will be changed to make the three values consistent;
- You cannot define the MTU and frame size separately -- they are always tied together by the emulation mode. This is not a restriction. Consider what this means. Perhaps you want to set the frame size to some large number and the MTU to some small number. The largest packet you can send is going to be limited by the MTU, so it is not possible to send a frame larger than the MTU plus overhead. The larger frame size is not useful.
So, if a user calls SetFrameSize, we assume that the maximum frame size is the interesting thing for that user and we just adjust the MTU to a new "correct value" based on the current encapsulation mode. If a user calls SetMtu, we assume that the MTU is the interesting property for that user, and we adjust the frame size to a new "correct value" for the current encapsulation mode. If a user calls SetEncapsulationMode, then we take the MTU as the free variable and set its value to match the current frame size.
- Parameters:
-
frameSize The max frame size of packets sent over this device.
| virtual void ns3::CsmaNetDevice::SetIfIndex | ( | const uint32_t | index | ) | [virtual] |
- Parameters:
-
index ifIndex of the device
Implements ns3::NetDevice.
| void ns3::CsmaNetDevice::SetInterframeGap | ( | Time | t | ) |
Set the inteframe gap used to separate packets. The interframe gap defines the minimum space required between packets sent by this device. As in Ethernet, it defaults to 96 bit times.
- Parameters:
-
t the interframe gap time
| virtual void ns3::CsmaNetDevice::SetLinkChangeCallback | ( | Callback< void > | callback | ) | [virtual] |
- Parameters:
-
callback the callback to invoke
Register a callback invoked whenever the link status changes to UP. This callback is typically used by the IP/ARP layer to flush the ARP cache whenever the link goes up.
Implements ns3::NetDevice.
| virtual bool ns3::CsmaNetDevice::SetMtu | ( | const uint16_t | mtu | ) | [virtual] |
- Parameters:
-
mtu MTU value, in bytes, to set for the device
- Returns:
- whether the MTU value was within legal bounds
Override for default MTU defined on a per-type basis.
Implements ns3::NetDevice.
| virtual void ns3::CsmaNetDevice::SetName | ( | const std::string | name | ) | [virtual] |
- Parameters:
-
name name of the device (e.g. "eth0")
Implements ns3::NetDevice.
Set the node to which this device is being attached.
Implements ns3::NetDevice.
| virtual void ns3::CsmaNetDevice::SetPromiscReceiveCallback | ( | PromiscReceiveCallback | cb | ) | [virtual] |
- Parameters:
-
cb callback to invoke whenever a packet has been received in promiscuous mode and must be forwarded to the higher layers.
Enables netdevice promiscuous mode and sets the callback that will handle promiscuous mode packets. Note, promiscuous mode packets means _all_ packets, including those packets that can be sensed by the netdevice but which are intended to be received by other hosts.
Implements ns3::NetDevice.
Attach a queue to the CsmaNetDevice.
The CsmaNetDevice "owns" a queue. This queue may be set by higher level topology objects to implement a particular queueing method such as DropTail or RED.
- See also:
- Queue
- DropTailQueue
- Parameters:
-
queue a Ptr to the queue for being assigned to the device.
| virtual void ns3::CsmaNetDevice::SetReceiveCallback | ( | NetDevice::ReceiveCallback | cb | ) | [virtual] |
Set the callback to be used to notify higher layers when a packet has been received.
- Parameters:
-
cb The callback.
Implements ns3::NetDevice.
| void ns3::CsmaNetDevice::SetReceiveEnable | ( | bool | enable | ) |
Enable or disable the receive side of the network device.
- Parameters:
-
enable Enable the receive side if true, otherwise disable.
| void ns3::CsmaNetDevice::SetReceiveErrorModel | ( | Ptr< ErrorModel > | em | ) |
Attach a receive ErrorModel to the CsmaNetDevice.
The CsmaNetDevice may optionally include an ErrorModel in the packet receive chain to simulate data errors in during transmission.
- See also:
- ErrorModel
- Parameters:
-
em a pointer to the ErrorModel
| void ns3::CsmaNetDevice::SetSendEnable | ( | bool | enable | ) |
Enable or disable the send side of the network device.
- Parameters:
-
enable Enable the send side if true, otherwise disable.
| virtual bool ns3::CsmaNetDevice::SupportsSendFrom | ( | void | ) | const [virtual] |
- Returns:
- true if this interface supports a bridging mode, false otherwise.
Implements ns3::NetDevice.
| void ns3::CsmaNetDevice::TransmitAbort | ( | void | ) | [private] |
Aborts the transmission of the current packet
If the net device has tried to transmit a packet for more times than the maximum allowed number of retries (channel always busy) then the packet is dropped.
| void ns3::CsmaNetDevice::TransmitCompleteEvent | ( | void | ) | [private] |
Stop Sending a Packet Down the Wire and Begin the Interframe Gap.
The TransmitCompleteEvent method is used internally to finish the process of sending a packet out on the channel. During execution of this method the TransmitEnd method is called on the channel to let it know that the physical device this class represents has finished sending simulated signals. The channel uses this event to begin its speed of light delay timer after which it notifies the Net Device(s) at the other end of the link that new bits have arrived (it delivers the Packet). During this method, the net device also schedules the TransmitReadyEvent at which time the transmitter becomes ready to send the next packet.
- See also:
- CsmaChannel::TransmitEnd ()
- TransmitReadyEvent ()
| void ns3::CsmaNetDevice::TransmitReadyEvent | ( | void | ) | [private] |
Cause the Transmitter to Become Ready to Send Another Packet.
The TransmitReadyEvent method is used internally to re-enable the transmit machine of the net device. It is scheduled after a suitable interframe gap after the completion of the previous transmission. The queue is checked at this time, and if there is a packet waiting on the queue, the transmission process is begun.
If a packet is in the queue, it is extracted for the queue as the next packet to be transmitted by the net device.
- See also:
- TransmitStart ()
| void ns3::CsmaNetDevice::TransmitStart | ( | ) | [private] |
Start Sending a Packet Down the Wire.
The TransmitStart method is the method that is used internally in the CsmaNetDevice to begin the process of sending a packet out on the channel. A corresponding method is called on the channel to let it know that the physical device this class represents has actually started sending signals, this causes the channel to enter the BUSY state. An event is scheduled for the time at which the bits have been completely transmitted.
If the channel is found to be BUSY, this method reschedules itself for execution at a later time (within the backoff period).
- See also:
- CsmaChannel::TransmitStart ()
- TransmitCompleteEvent ()
Member Data Documentation
Mac48Address ns3::CsmaNetDevice::m_address [private] |
The MAC address which has been assigned to this device.
Backoff ns3::CsmaNetDevice::m_backoff [private] |
Holds the backoff parameters and is used to calculate the next backoff time to use when the channel is busy and the net device is ready to transmit
DataRate ns3::CsmaNetDevice::m_bps [private] |
The data rate that the Net Device uses to simulate packet transmission timing.
- See also:
- class DataRate
Ptr<CsmaChannel> ns3::CsmaNetDevice::m_channel [private] |
The CsmaChannel to which this CsmaNetDevice has been attached.
- See also:
- class CsmaChannel
Ptr<Packet> ns3::CsmaNetDevice::m_currentPkt [private] |
Next packet that will be transmitted (if transmitter is not currently transmitting) or packet that is currently being transmitted.
uint32_t ns3::CsmaNetDevice::m_deviceId [private] |
Device ID returned by the attached functions. It is used by the mp-channel to identify each net device to make sure that only active net devices are writing to the channel
TracedCallback<Ptr<const Packet> > ns3::CsmaNetDevice::m_dropTrace [private] |
The trace source for the packet drop events that the device can fire.
- See also:
- class CallBackTraceSource
The type of packet that should be created by the AddHeader function and that should be processed by the ProcessHeader function.
uint32_t ns3::CsmaNetDevice::m_frameSize [private] |
The frame size/packet size. This corresponds to the maximum number of bytes that can be transmitted as a packet without framing. This corresponds to the 1518 byte packet size often seen on Ethernet.
uint32_t ns3::CsmaNetDevice::m_ifIndex [private] |
The interface index (really net evice index) that has been assigned to this network device.
Callback<void> ns3::CsmaNetDevice::m_linkChangeCallback [private] |
Callback to fire if the link changes state (up or down).
bool ns3::CsmaNetDevice::m_linkUp [private] |
Flag indicating whether or not the link is up. In this case, whether or not the device is connected to a channel.
uint32_t ns3::CsmaNetDevice::m_mtu [private] |
The Maxmimum Transmission Unit. This corresponds to the maximum number of bytes that can be transmitted as seen from higher layers. This corresponds to the 1500 byte MTU size often seen on IP over Ethernet.
std::string ns3::CsmaNetDevice::m_name [private] |
The human readable name of this device.
Ptr<Node> ns3::CsmaNetDevice::m_node [private] |
The Node to which this device is attached.
The callback used to notify higher layers that a packet has been received in promiscuous mode.
Ptr<Queue> ns3::CsmaNetDevice::m_queue [private] |
The Queue which this CsmaNetDevice uses as a packet source. Management of this Queue has been delegated to the CsmaNetDevice and it has the responsibility for deletion.
- See also:
- class Queue
- class DropTailQueue
bool ns3::CsmaNetDevice::m_receiveEnable [private] |
Enable net device to receive packets. True by default
Ptr<ErrorModel> ns3::CsmaNetDevice::m_receiveErrorModel [private] |
Error model for receive packet events
The callback used to notify higher layers that a packet has been received.
TracedCallback<Ptr<const Packet> > ns3::CsmaNetDevice::m_rxTrace [private] |
The trace source for the packet reception events that the device can fire.
- See also:
- class CallBackTraceSource
bool ns3::CsmaNetDevice::m_sendEnable [private] |
Enable net device to send packets. True by default
Time ns3::CsmaNetDevice::m_tInterframeGap [private] |
The interframe gap that the Net Device uses insert time between packet transmission
- See also:
- class Time
The state of the Net Device transmit state machine.
- See also:
- TxMachineState
The documentation for this class was generated from the following files:
- src/devices/csma/csma-net-device.h
- doc/introspected-doxygen.h
 1.7.1
1.7.1