Wireless jamming model: Difference between revisions
(→Usage) |
|||
| Line 85: | Line 85: | ||
= Usage = | = Usage = | ||
Coming soon. | |||
= Schedule = | = Schedule = | ||
Revision as of 02:00, 21 April 2010
General
Network Security Lab, University of Washington, Seattle has begun work on a wireless interference (jamming) model for ns3. The goal is to to enable researchers to use ns3 to study jamming and its mitigation methods.
Project Background
Interference (Jamming) in wireless networks is an important example of malicious attacks in wireless networks. It is achieved by deliberate transmission of radio signals to disrupt the communication in a wireless network by decreasing the signal-to-interference-noise ratio (SINR). Jamming leads to corrupted packets at the receiver, which results a lowered throughput.
Project Goals
To provide a simulation toolkit that allows researchers to easily implement and simulate a wireless jamming strategy or jamming detection/mitigation strategy. To enable researchers to evaluate the performances of jamming and jamming detection/mitigation strategies.
Jammer
Jammer is one of the key elements in the jamming model. It includes the following primitives to enable implementation of different jamming strategies:
- Transmit jamming signal.
- Adjust jamming power & duration.
- Extract packet headers.
- Scan, hop channels (for a multi-channel wireless protocol).
- etc.
Honest Nodes
A set of primitives is added to honest nodes to enable implementation jamming detection/mitigation strategies:
- Measure Packet Delivery Ratio (PDR).
- Measure Received Signal Strength (RSS).
- Scan, hop channels (for a multi-channel wireless protocol).
- etc.
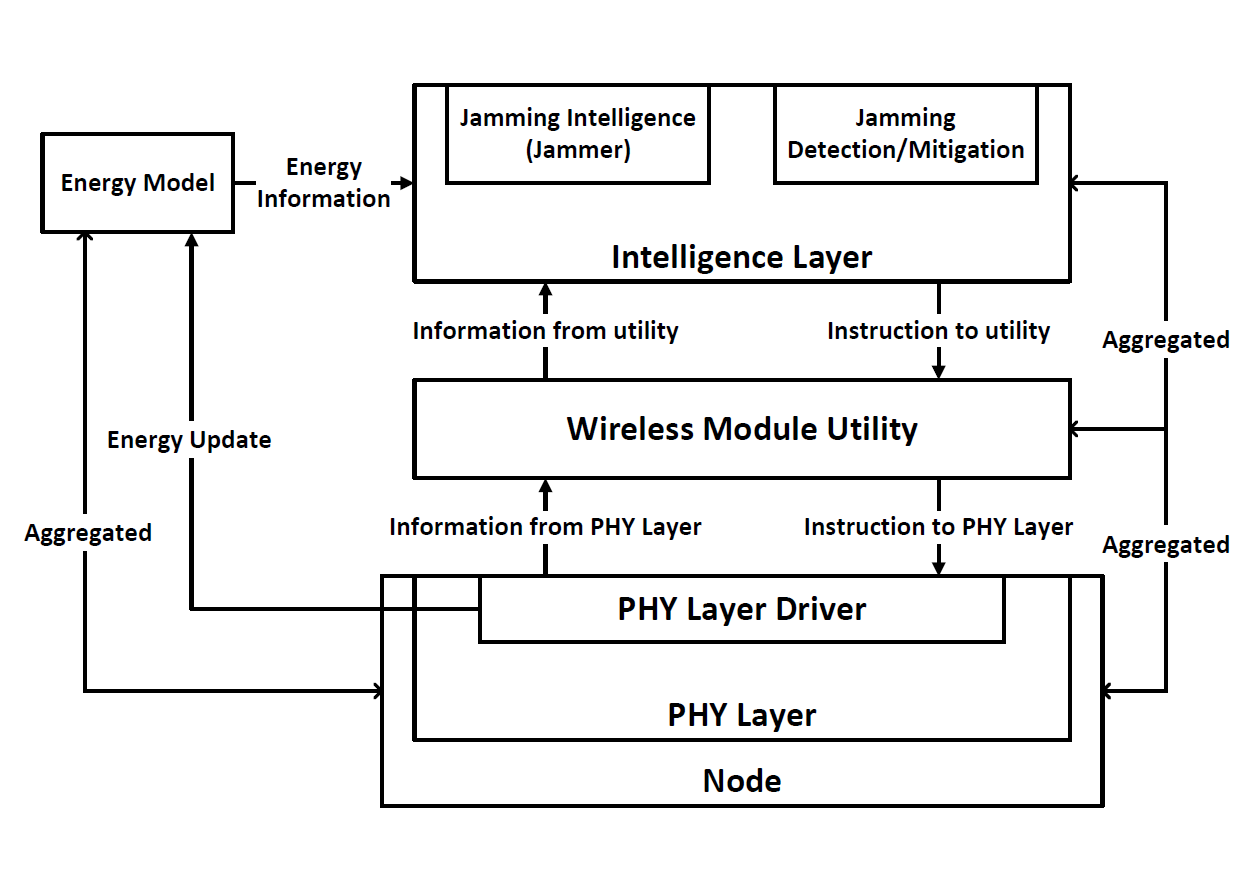
Jamming Model Hierarchy
The jamming model is designed to minimize its dependency on the physical (PHY) layer of the wireless protocol. It consists of the following components:
- Jamming intelligence (jammer).
- This base class provides interfaces to wireless module utility.
- Detailed jamming strategies such as constant jammer, reactive jammer etc. are implemented in child classes.
- This class depends on the wireless module utility class.
- Jamming detection/mitigation intelligence (mitigation).
- This base class provides interfaces to wireless module utility.
- Detailed jamming detection/mitigation strategies such as mitigate by channel hop, are implemented in child classes.
- This class depends on the wireless module utility class.
- Wireless module utility (utility).
- This class provides a set of functions for jammer and jamming mitigation classes to utilize for implementing their strategies.
- This class acts as a bridge between the intelligence layer and the PHY layer, separating the intelligence from PHY layer details.
- PHY layer driver (driver).
- Modification to PHY layer classes are required to provide interface to the utility.
- The modifications are specific to the PHY layer class one wants to study on.
- Driver also provides an interface to the energy model.
Jamming Intelligence (Jammer)
The following types of jammers are provided by the jamming model:
- Eavesdropper jammer.
- Listens and records wireless traffic in channel(s).
- Constant jammer.
- Sends jamming signal of certain duration at a constant interval.
- Random jammer.
- Sends jamming signal of certain duration at a randomly chosen interval.
- Reactive jammer.
- Sends jamming signal of certain duration only when communication is present in the channel.
Users can easily define their own jamming strategies (classes) following the format in provided classes. The jamming intelligence class is designed to abstract the detail of sending jamming signals and extracting information from the channel.
Jamming Detection/Mitigation Intelligence
The following jamming detection strategies are provided by the jamming model:
- Detect jamming by RSS.
- Detect jamming by PDR.
- Detect jamming by RSS & PDR.
The following jamming mitigation strategies are provided by the jamming model:
- Mitigate by channel hop.
- When jamming is detected, honest nodes hop onto a different channel (given a multi-channel wireless protocol) to avoid being jammed.
Users can easily define their own jamming detection/mitigation strategies (classes) following the format in provided classes. The jamming detection/mitigation class is designed to abstract the detail of extracting information from the channel.
Wireless Module Utility
This class provides essential functions for jamming intelligence and jamming detection/mitigation intelligence to operate. It can also be installed separately for monitoring network performance.
PHY Layer Driver
Modifications of the PHY layer is required to pass information to the wireless module utility. Currently, only drivers for the Wifi class is provided.
Usage
Coming soon.
Schedule
- 4/19/2010 - 4/30/2010: Private review.