SOCIS2016: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 67: | Line 67: | ||
The uplink channel, from OGS to GEO, requires a separate loss model and is not yet implemented. The two links are asymmetric due to the difference in proximity of the transmitter to the atmosphere. In the uplink case, the concentrated beam is much more susceptible to refraction when compared with the downlink. The downlink beam can be modeled as a planar wave as it enters the atmosphere. | The uplink channel, from OGS to GEO, requires a separate loss model and is not yet implemented. The two links are asymmetric due to the difference in proximity of the transmitter to the atmosphere. In the uplink case, the concentrated beam is much more susceptible to refraction when compared with the downlink. The downlink beam can be modeled as a planar wave as it enters the atmosphere. | ||
'''Propagation Loss Model''' | |||
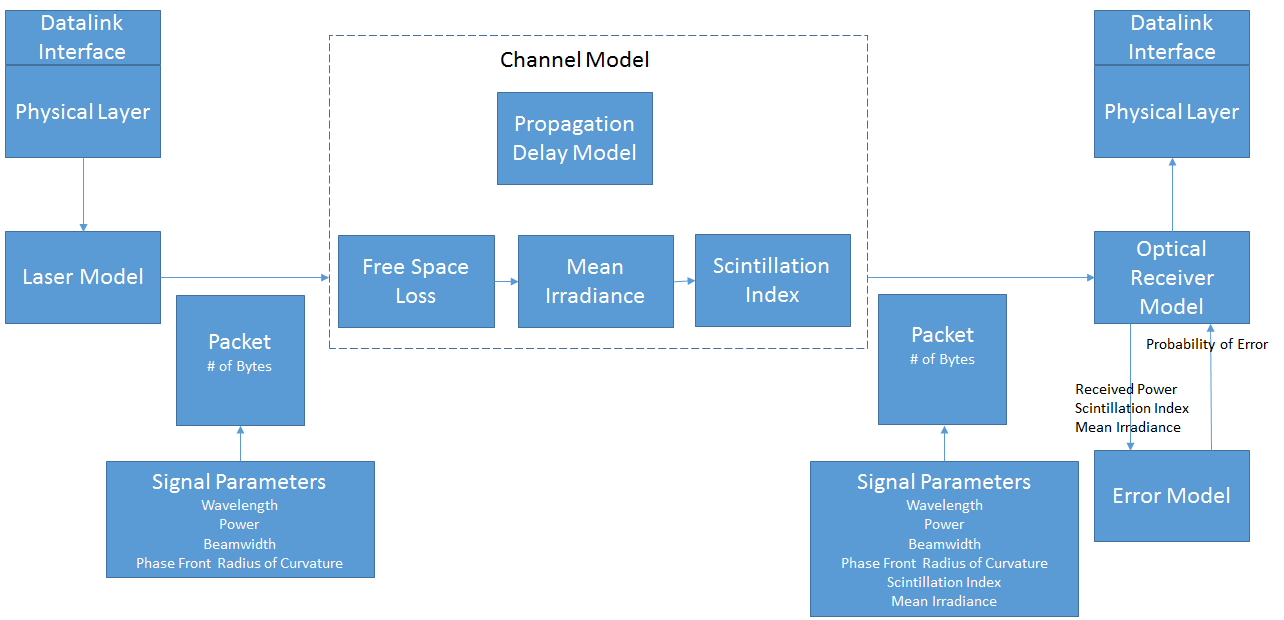
The propagation loss model is divided into a chain of individual models as shown in the block diagram. The free space loss applies a reduction in power due to free space propagation, the mean irradiance is computed, and finally the scintillation index is calculated. Each of these values are applied to the FsoSignalParameters struct which is sent along with the packet. To include weather effects, such as losses due to rain, one can add another loss model to the chain. | |||
'''Antenna Model''' | '''Antenna Model''' | ||
Revision as of 21:32, 15 July 2016
Main Page - Roadmap - Summer Projects - Project Ideas - Developer FAQ - Tools - Related Projects
HOWTOs - Installation - Troubleshooting - User FAQ - Samples - Models - Education - Contributed Code - Papers
Return to Summer Projects page.
ns-3 is participating in the 2016 ESA Summer of Code in Space with one student project.
Project overview
- Project: Optical satellite systems
- Student: Michael Di Perna
- Mentors: Jani Puttonen, Tommaso Pecarolla, Tom Henderson
- Code: https://github.com/Skyline101/ns-3-dev-git-fso
- About me: I am a masters student (electrical engineering) in my final year at Concordia University (Montreal, CA). My field of research is in optimal control of single and multi-agent systems. I have experience in both aerospace and robotics fields. My personal research interests include spacecraft and communication networks.
Project goals
This project's goal is to provide the foundation to simulate optical satellite systems, such as the European Data Relay System (EDRS), for future researchers to build upon. The main focus of this project will be to develop the channel models between a GEO satellite and an optical ground station (OGS) and between a GEO and LEO satellite. The project should provide the following upon completion:
- An atmospheric model for the GEO to OGS channel
- Capability to simulate different weather conditions (i.e. fog or rain)
- A mobility model for the satellites
- An implementation of a Space Data Link Protocol (SDLP) (time permitting)
Schedule
The project will span 13 weeks and is organized as follows.
Project Definition1 Week
- Familiarize with ns-3 simulator
- Investigate Data Link layer protocols (SDLP)
Channel Model Research 2 Weeks
- Research channel models for optical satellite systems
- Begin documentation of model and code structure
Channel Model Integration 2 Weeks
- Integrate channel model with ns-3
- Test channel model (test cases and comparisons with experimental data)
- Documentation
Mobility Model Research 2 Weeks
- Investigate currently available satellite mobility models
- Begin documentation of model and code structure
Channel Model Integration 2 Weeks
- Integrate satellite mobility model with ns-3
- Test mobility model (test cases and comparisons with experimental data)
- Documentation
Data Link Layer Structure 1 Week
- Code structure for either AOS or TM SDLP
Data Link Layer Implementation 2 Weeks
- Implement the selected SDLP in ns-3
- Documentation and testing
Project Buffer/Maintenance 1 Week
- Project documentation
- Finish ns-3 integration
Milestones
Channel Model
A new propagation loss model has been added (FsoPropagationLossModel) which models the losses in the downlink of a GEO to OGS link. The FsoChannel is a container class which contains pointers to the loss model as well as the RX/TX and delay model.
As the optical beam propagates through the atmosphere it is refracted in pockets of turbulence. This process, known as scintillation, causes the irradiance of the beam to vary stochastically at the receiver. The loss model uses the Hufnagel-Valley (HV) model to determine the index of refraction of the atmosphere as a function of altitude. The HV model is then used to calculate the scintillation index which is used to determine the parameters of a log-normal distribution for the irradiance at the receiver.
The uplink channel, from OGS to GEO, requires a separate loss model and is not yet implemented. The two links are asymmetric due to the difference in proximity of the transmitter to the atmosphere. In the uplink case, the concentrated beam is much more susceptible to refraction when compared with the downlink. The downlink beam can be modeled as a planar wave as it enters the atmosphere.
Propagation Loss Model
The propagation loss model is divided into a chain of individual models as shown in the block diagram. The free space loss applies a reduction in power due to free space propagation, the mean irradiance is computed, and finally the scintillation index is calculated. Each of these values are applied to the FsoSignalParameters struct which is sent along with the packet. To include weather effects, such as losses due to rain, one can add another loss model to the chain.
Antenna Model
A new antenna model, LaserAntennaModel, has been created for the project. It contains the beamwidth (meters) which represents the distance from the beam axis at which the amplitude drops to 1/e, and the phase front radius of curvature (meters) which characterizes the shape of the beam (convergent, divergent, or collimated).
Error Model
The error model under consideration involves a two tier model: a packet level and a link model. The packet level error model provides a mean bit error rate (BER) based on the use of on-off keying (OOK). The mean BER is used to provide the probability of error to the physical layer and may be considered constant should the atmospheric conditions remain constant. The link error model takes into consideration fades which drop the irradiance at the receiver below a specified threshold. The mean fade time provides a mean duration for which the irradiance may stay below this threshold. During this time period any packets being received would be lost. The mean fade time can vary from 1 millisecond to 10's of microseconds depending on the threshold.
Physical Layer
The Consultative Committee for Space Data Systems (CCSDS) are currently considering a physical layer standard for optical communication systems for space applications. We hope to obtain suggestions from the optical group to guide our model of the physical layer.
- First code review: (date TBD; code TBD)
- Final code review: (date TBD; code TBD)