PyViz: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
(updated installation instructions for NS 3.8) |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
# [http://code.nsnam.org/gjc/ns-3-pyviz/ gjc/ns-3-pyviz]: this branch is based on the old NS-3.2 version; | # [http://code.nsnam.org/gjc/ns-3-pyviz/ gjc/ns-3-pyviz]: this branch is based on the old NS-3.2 version; | ||
# [http://code.nsnam.org/gjc/ns-3.7-pyviz/ gjc/ns-3.7-pyviz]: this branch is based on NS-3.7 | # [http://code.nsnam.org/gjc/ns-3.7-pyviz/ gjc/ns-3.7-pyviz]: this branch is based on NS-3.7 | ||
# [http://code.nsnam.org/gjc/ns-3.7-pyviz/ gjc/ns-3.8-pyviz]: this branch is based on NS-3.8 | |||
# [http://code.nsnam.org/gjc/ns-3-pyviz-dev/ gjc/ns-3-pyviz-dev]: this branch is based on the current NS-3 development version, ns-3-dev. | # [http://code.nsnam.org/gjc/ns-3-pyviz-dev/ gjc/ns-3-pyviz-dev]: this branch is based on the current NS-3 development version, ns-3-dev. | ||
You will have to select one of those branches | You will have to select one of those branches, and [http://hgbook.red-bean.com/read/a-tour-of-mercurial-merging-work.html merge] it with your code. | ||
You will need to have certain python modules installed. Following installation instructions (for Ubuntu): | You will need to have certain python modules installed. Following installation instructions (for Ubuntu): | ||
sudo apt-get install python-pygraphviz python-kiwi python-pygoocanvas python-gnome2 python-gnomedesktop python-rsvg | sudo apt-get install python-dev python-pygraphviz python-kiwi python-pygoocanvas \ | ||
python-gnome2 python-gnomedesktop python-rsvg | |||
Optionally, you may install Interactive Python in order to have a Console button in the visualizer GUI: | Optionally, you may install Interactive Python in order to have a Console button in the visualizer GUI: | ||
Revision as of 11:42, 14 May 2010
Introduction
NS-3 PyViz is a live simulation visualizer, meaning that it uses no trace files. It can be most useful for debugging purposes, i.e. to figure out if mobility models are what you expect, where packets are being dropped, etc. There's also a builtin interactive python console that can be used to debug the state of the running objects. Although it is mostly written in Python, it works both with Python and pure C++ simulations.
Installation
PyViz is not integrated into mainline NS-3, it is found on a separate branch. There are actually 2 branches of PyViz:
- gjc/ns-3-pyviz: this branch is based on the old NS-3.2 version;
- gjc/ns-3.7-pyviz: this branch is based on NS-3.7
- gjc/ns-3.8-pyviz: this branch is based on NS-3.8
- gjc/ns-3-pyviz-dev: this branch is based on the current NS-3 development version, ns-3-dev.
You will have to select one of those branches, and merge it with your code.
You will need to have certain python modules installed. Following installation instructions (for Ubuntu):
sudo apt-get install python-dev python-pygraphviz python-kiwi python-pygoocanvas \
python-gnome2 python-gnomedesktop python-rsvg
Optionally, you may install Interactive Python in order to have a Console button in the visualizer GUI:
sudo apt-get install ipython
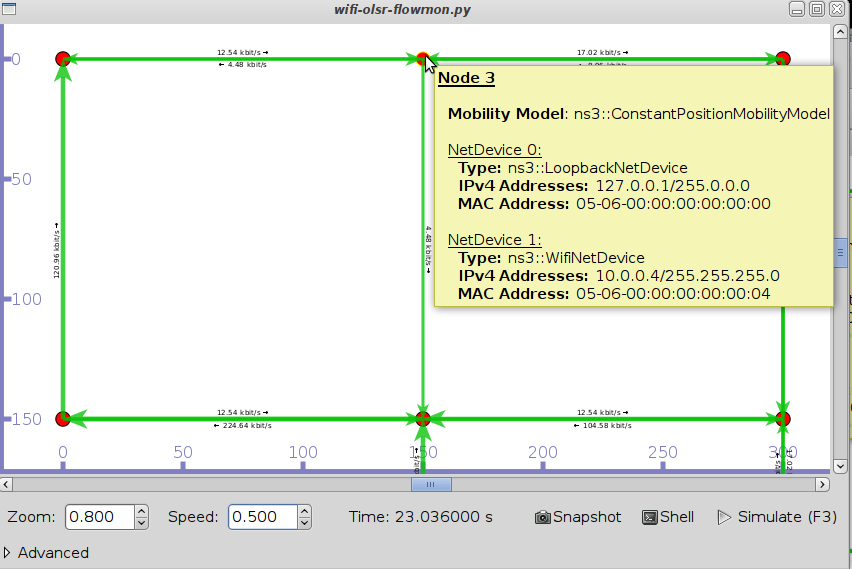
Configure and build your ns-3 tree as usual. You can test the visualizer for example with the FlowMonitor sample program:
./waf --pyrun examples/flowmon/wifi-olsr-flowmon.py
And the result should be:
Enabling the visualizer in your own simulation
For Python simulations, you have to import the visualizer module, and call visualizer.start() instead of ns3.Simulator.Run(). For example, like this.
For C++ simulations, #include "ns3/visualizer.h", and replace the call to Simulator::Run (); with Visualizer::Run ();. For example, like this.
Usage Tips
The mouse controls work as follows:
- Middle button drag:
- Over a Node, drags the Node around (calls SetPosition on the mobility model of the node, beware the certain mobility models have bounds and crash if the bounds are not respected);
- Over the background: scroll the view;
- First button: select a Node, if over the node;
- Scroll wheel: zoom in/out
In the shell, a couple of variables are defined:
- 'viz': the visualizer python class, which has some useful methods;
- 'selected_node': the currently selected NS-3 node.
Known problems
PyViz does not detect WiMax transmissions due to a bug in WimaxNetDevice.