ns3::TcpSocketBase Class Reference
[Socket, Tcp]
A base class for implementation of a stream socket using TCP. More...
#include <tcp-socket-base.h>
Public Member Functions | |
| TcpSocketBase (void) | |
| TcpSocketBase (const TcpSocketBase &sock) | |
| virtual void | SetNode (Ptr< Node > node) |
| virtual void | SetTcp (Ptr< TcpL4Protocol > tcp) |
| virtual void | SetRtt (Ptr< RttEstimator > rtt) |
| virtual enum SocketErrno | GetErrno (void) const |
| virtual enum SocketType | GetSocketType (void) const |
| virtual Ptr< Node > | GetNode (void) const |
| virtual int | Bind (void) |
| virtual int | Bind (const Address &address) |
| virtual int | Connect (const Address &address) |
| Initiate a connection to a remote host. | |
| virtual int | Listen (void) |
| Listen for incoming connections. | |
| virtual int | Close (void) |
| Close a socket. | |
| virtual int | ShutdownSend (void) |
| virtual int | ShutdownRecv (void) |
| virtual int | Send (Ptr< Packet > p, uint32_t flags) |
| Send data (or dummy data) to the remote host. | |
| virtual int | SendTo (Ptr< Packet > p, uint32_t flags, const Address &toAddress) |
| Send data to a specified peer. | |
| virtual Ptr< Packet > | Recv (uint32_t maxSize, uint32_t flags) |
| Read data from the socket. | |
| virtual Ptr< Packet > | RecvFrom (uint32_t maxSize, uint32_t flags, Address &fromAddress) |
| Read a single packet from the socket and retrieve the sender address. | |
| virtual uint32_t | GetTxAvailable (void) const |
| Returns the number of bytes which can be sent in a single call to Send. | |
| virtual uint32_t | GetRxAvailable (void) const |
| virtual int | GetSockName (Address &address) const |
| virtual void | BindToNetDevice (Ptr< NetDevice > netdevice) |
| Bind a socket to specific device. | |
Static Public Member Functions | |
| static TypeId | GetTypeId (void) |
| This method returns the TypeId associated to ns3::TcpSocketBase. | |
Protected Member Functions | |
| virtual void | SetSndBufSize (uint32_t size) |
| virtual uint32_t | GetSndBufSize (void) const |
| virtual void | SetRcvBufSize (uint32_t size) |
| virtual uint32_t | GetRcvBufSize (void) const |
| virtual void | SetSegSize (uint32_t size) |
| virtual uint32_t | GetSegSize (void) const |
| virtual void | SetSSThresh (uint32_t threshold)=0 |
| virtual uint32_t | GetSSThresh (void) const =0 |
| virtual void | SetInitialCwnd (uint32_t cwnd)=0 |
| virtual uint32_t | GetInitialCwnd (void) const =0 |
| virtual void | SetConnTimeout (Time timeout) |
| virtual Time | GetConnTimeout (void) const |
| virtual void | SetConnCount (uint32_t count) |
| virtual uint32_t | GetConnCount (void) const |
| virtual void | SetDelAckTimeout (Time timeout) |
| virtual Time | GetDelAckTimeout (void) const |
| virtual void | SetDelAckMaxCount (uint32_t count) |
| virtual uint32_t | GetDelAckMaxCount (void) const |
| virtual void | SetPersistTimeout (Time timeout) |
| virtual Time | GetPersistTimeout (void) const |
| virtual bool | SetAllowBroadcast (bool allowBroadcast) |
| Configure whether broadcast datagram transmissions are allowed. | |
| virtual bool | GetAllowBroadcast () const |
| Query whether broadcast datagram transmissions are allowed. | |
| int | SetupCallback (void) |
| int | DoConnect (void) |
| void | ConnectionSucceeded (void) |
| int | SetupEndpoint (void) |
| void | CompleteFork (Ptr< Packet >, const TcpHeader &, const Address &fromAddress, const Address &toAdress) |
| void | ForwardUp (Ptr< Packet > packet, Ipv4Header header, uint16_t port, Ptr< Ipv4Interface > incomingInterface) |
| bool | SendPendingData (bool withAck=false) |
| void | SendEmptyPacket (uint8_t flags) |
| void | SendRST (void) |
| bool | OutOfRange (SequenceNumber32 s) const |
| int | DoClose (void) |
| void | CloseAndNotify (void) |
| void | Destroy (void) |
| void | DeallocateEndPoint (void) |
| void | PeerClose (Ptr< Packet >, const TcpHeader &) |
| void | DoPeerClose (void) |
| void | CancelAllTimers (void) |
| void | ProcessEstablished (Ptr< Packet >, const TcpHeader &) |
| void | ProcessListen (Ptr< Packet >, const TcpHeader &, const Address &, const Address &) |
| void | ProcessSynSent (Ptr< Packet >, const TcpHeader &) |
| void | ProcessSynRcvd (Ptr< Packet >, const TcpHeader &, const Address &, const Address &) |
| void | ProcessWait (Ptr< Packet >, const TcpHeader &) |
| void | ProcessClosing (Ptr< Packet >, const TcpHeader &) |
| void | ProcessLastAck (Ptr< Packet >, const TcpHeader &) |
| virtual uint32_t | UnAckDataCount (void) |
| virtual uint32_t | BytesInFlight (void) |
| virtual uint32_t | Window (void) |
| virtual uint32_t | AvailableWindow (void) |
| virtual uint16_t | AdvertisedWindowSize (void) |
| virtual Ptr< TcpSocketBase > | Fork (void)=0 |
| virtual void | ReceivedAck (Ptr< Packet >, const TcpHeader &) |
| virtual void | ReceivedData (Ptr< Packet >, const TcpHeader &) |
| virtual void | EstimateRtt (const TcpHeader &) |
| virtual void | NewAck (SequenceNumber32 const &seq) |
| virtual void | DupAck (const TcpHeader &t, uint32_t count)=0 |
| virtual void | ReTxTimeout (void) |
| virtual void | Retransmit (void) |
| virtual void | DelAckTimeout (void) |
| virtual void | LastAckTimeout (void) |
| virtual void | PersistTimeout (void) |
| virtual void | DoRetransmit (void) |
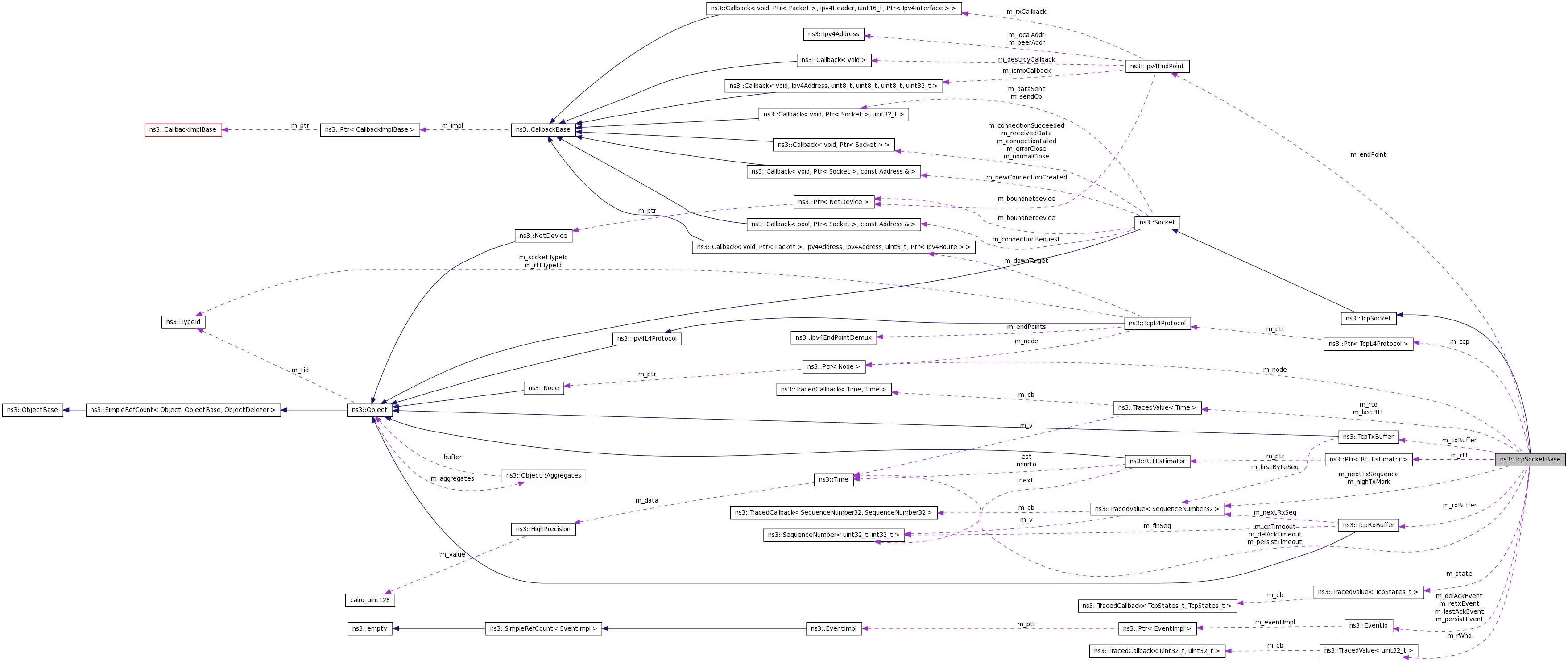
Protected Attributes | |
| EventId | m_retxEvent |
| EventId | m_lastAckEvent |
| EventId | m_delAckEvent |
| EventId | m_persistEvent |
| uint32_t | m_dupAckCount |
| uint32_t | m_delAckCount |
| uint32_t | m_delAckMaxCount |
| uint32_t | m_cnCount |
| TracedValue< Time > | m_rto |
| TracedValue< Time > | m_lastRtt |
| Time | m_delAckTimeout |
| Time | m_persistTimeout |
| Time | m_cnTimeout |
| Ipv4EndPoint * | m_endPoint |
| Ptr< Node > | m_node |
| Ptr< TcpL4Protocol > | m_tcp |
| Ptr< RttEstimator > | m_rtt |
| TracedValue< SequenceNumber32 > | m_nextTxSequence |
| TracedValue< SequenceNumber32 > | m_highTxMark |
| TcpRxBuffer | m_rxBuffer |
| TcpTxBuffer | m_txBuffer |
| TracedValue< TcpStates_t > | m_state |
| enum SocketErrno | m_errno |
| bool | m_closeNotified |
| bool | m_closeOnEmpty |
| bool | m_shutdownSend |
| bool | m_shutdownRecv |
| bool | m_connected |
| uint32_t | m_segmentSize |
| TracedValue< uint32_t > | m_rWnd |
Detailed Description
A base class for implementation of a stream socket using TCP.
This class contains the essential components of TCP, as well as a sockets interface for upper layers to call. This serves as a base for other TCP functions where the sliding window mechanism is handled here. This class provides connection orientation and sliding window flow control. Part of this class is modified from the original NS-3 TCP socket implementation (TcpSocketImpl) by Raj Bhattacharjea.
Constructor & Destructor Documentation
| ns3::TcpSocketBase::TcpSocketBase | ( | void | ) |
Create an unbound TCP socket
| ns3::TcpSocketBase::TcpSocketBase | ( | const TcpSocketBase & | sock | ) |
Clone a TCP socket, for use upon receiving a connection request in LISTEN state
Member Function Documentation
| virtual int ns3::TcpSocketBase::Bind | ( | const Address & | address | ) | [virtual] |
- Parameters:
-
address the address to try to allocate
- Returns:
- 0 on success, -1 on failure.
Allocate a local endpoint for this socket.
Implements ns3::Socket.
| virtual int ns3::TcpSocketBase::Bind | ( | void | ) | [virtual] |
Allocate a local endpoint for this socket.
- Returns:
- 0 on success, -1 on failure.
Implements ns3::Socket.
Bind a socket to specific device.
This method corresponds to using setsockopt() SO_BINDTODEVICE of real network or BSD sockets. If set on a socket, this option will force packets to leave the bound device regardless of the device that IP routing would naturally choose. In the receive direction, only packets received from the bound interface will be delivered.
This option has no particular relationship to binding sockets to an address via Socket::Bind (). It is possible to bind sockets to a specific IP address on the bound interface by calling both Socket::Bind (address) and Socket::BindToNetDevice (device), but it is also possible to bind to mismatching device and address, even if the socket can not receive any packets as a result.
- Parameters:
-
netdevice Pointer to Netdevice of desired interface
- Returns:
- nothing
Reimplemented from ns3::Socket.
| virtual int ns3::TcpSocketBase::Close | ( | void | ) | [virtual] |
Close a socket.
- Returns:
- zero on success, -1 on failure.
After the Close call, the socket is no longer valid, and cannot safely be used for subsequent operations.
Implements ns3::Socket.
| virtual int ns3::TcpSocketBase::Connect | ( | const Address & | address | ) | [virtual] |
Initiate a connection to a remote host.
- Parameters:
-
address Address of remote.
Implements ns3::Socket.
Reimplemented in ns3::TcpNewReno, ns3::TcpReno, and ns3::TcpTahoe.
| virtual bool ns3::TcpSocketBase::GetAllowBroadcast | ( | ) | const [protected, virtual] |
Query whether broadcast datagram transmissions are allowed.
This method corresponds to using getsockopt() SO_BROADCAST of real network or BSD sockets.
- Returns:
- true if broadcast is allowed, false otherwise
Implements ns3::Socket.
| virtual enum SocketErrno ns3::TcpSocketBase::GetErrno | ( | void | ) | const [virtual] |
- Returns:
- the errno associated to the last call which failed in this socket. Each socket's errno is initialized to zero when the socket is created.
Implements ns3::Socket.
- Returns:
- the node this socket is associated with.
Implements ns3::Socket.
| virtual uint32_t ns3::TcpSocketBase::GetRxAvailable | ( | void | ) | const [virtual] |
Return number of bytes which can be returned from one or multiple calls to Recv. Must be possible to call this method from the Recv callback.
Implements ns3::Socket.
| virtual enum SocketType ns3::TcpSocketBase::GetSocketType | ( | void | ) | const [virtual] |
- Returns:
- the socket type, analogous to getsockopt (SO_TYPE)
Implements ns3::Socket.
| virtual int ns3::TcpSocketBase::GetSockName | ( | Address & | address | ) | const [virtual] |
- Parameters:
-
address the address name this socket is associated with.
- Returns:
- 0 if success, -1 otherwise
Implements ns3::Socket.
| virtual uint32_t ns3::TcpSocketBase::GetTxAvailable | ( | void | ) | const [virtual] |
Returns the number of bytes which can be sent in a single call to Send.
For datagram sockets, this returns the number of bytes that can be passed atomically through the underlying protocol.
For stream sockets, this returns the available space in bytes left in the transmit buffer.
Implements ns3::Socket.
| static TypeId ns3::TcpSocketBase::GetTypeId | ( | void | ) | [static] |
This method returns the TypeId associated to ns3::TcpSocketBase.
This object is accessible through the following paths with Config::Set and Config::Connect:
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::AlohaNoackNetDevice/Phy/$ns3::Ipv4L4Protocol/$ns3::TcpL4Protocol/SocketList/[i]
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::AlohaNoackNetDevice/Phy/$ns3::TcpL4Protocol/SocketList/[i]
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::AlohaNoackNetDevice/Phy/$ns3::TcpSocket/$ns3::TcpSocketBase
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::AlohaNoackNetDevice/Phy/$ns3::TcpSocketBase
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::BaseStationNetDevice/BsIpcsPacketClassifier/$ns3::Ipv4L4Protocol/$ns3::TcpL4Protocol/SocketList/[i]
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::BaseStationNetDevice/BsIpcsPacketClassifier/$ns3::TcpL4Protocol/SocketList/[i]
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::BaseStationNetDevice/BsIpcsPacketClassifier/$ns3::TcpSocket/$ns3::TcpSocketBase
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::BaseStationNetDevice/BsIpcsPacketClassifier/$ns3::TcpSocketBase
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::BaseStationNetDevice/LinkManager/$ns3::Ipv4L4Protocol/$ns3::TcpL4Protocol/SocketList/[i]
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::BaseStationNetDevice/LinkManager/$ns3::TcpL4Protocol/SocketList/[i]
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::BaseStationNetDevice/LinkManager/$ns3::TcpSocket/$ns3::TcpSocketBase
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::BaseStationNetDevice/LinkManager/$ns3::TcpSocketBase
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::BaseStationNetDevice/SSManager/$ns3::Ipv4L4Protocol/$ns3::TcpL4Protocol/SocketList/[i]
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::BaseStationNetDevice/SSManager/$ns3::TcpL4Protocol/SocketList/[i]
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::BaseStationNetDevice/SSManager/$ns3::TcpSocket/$ns3::TcpSocketBase
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::BaseStationNetDevice/SSManager/$ns3::TcpSocketBase
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::BaseStationNetDevice/ServiceFlowManager/$ns3::Ipv4L4Protocol/$ns3::TcpL4Protocol/SocketList/[i]
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::BaseStationNetDevice/ServiceFlowManager/$ns3::TcpL4Protocol/SocketList/[i]
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::BaseStationNetDevice/ServiceFlowManager/$ns3::TcpSocket/$ns3::TcpSocketBase
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::BaseStationNetDevice/ServiceFlowManager/$ns3::TcpSocketBase
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::NonCommunicatingNetDevice/Phy/$ns3::Ipv4L4Protocol/$ns3::TcpL4Protocol/SocketList/[i]
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::NonCommunicatingNetDevice/Phy/$ns3::TcpL4Protocol/SocketList/[i]
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::NonCommunicatingNetDevice/Phy/$ns3::TcpSocket/$ns3::TcpSocketBase
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::NonCommunicatingNetDevice/Phy/$ns3::TcpSocketBase
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::SubscriberStationNetDevice/Classifier/$ns3::Ipv4L4Protocol/$ns3::TcpL4Protocol/SocketList/[i]
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::SubscriberStationNetDevice/Classifier/$ns3::TcpL4Protocol/SocketList/[i]
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::SubscriberStationNetDevice/Classifier/$ns3::TcpSocket/$ns3::TcpSocketBase
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::SubscriberStationNetDevice/Classifier/$ns3::TcpSocketBase
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::SubscriberStationNetDevice/LinkManager/$ns3::Ipv4L4Protocol/$ns3::TcpL4Protocol/SocketList/[i]
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::SubscriberStationNetDevice/LinkManager/$ns3::TcpL4Protocol/SocketList/[i]
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::SubscriberStationNetDevice/LinkManager/$ns3::TcpSocket/$ns3::TcpSocketBase
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::SubscriberStationNetDevice/LinkManager/$ns3::TcpSocketBase
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::SubscriberStationNetDevice/SSScheduler/$ns3::Ipv4L4Protocol/$ns3::TcpL4Protocol/SocketList/[i]
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::SubscriberStationNetDevice/SSScheduler/$ns3::TcpL4Protocol/SocketList/[i]
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::SubscriberStationNetDevice/SSScheduler/$ns3::TcpSocket/$ns3::TcpSocketBase
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::SubscriberStationNetDevice/SSScheduler/$ns3::TcpSocketBase
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::UanNetDevice/Channel/NoiseModel/$ns3::Ipv4L4Protocol/$ns3::TcpL4Protocol/SocketList/[i]
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::UanNetDevice/Channel/NoiseModel/$ns3::TcpL4Protocol/SocketList/[i]
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::UanNetDevice/Channel/NoiseModel/$ns3::TcpSocket/$ns3::TcpSocketBase
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::UanNetDevice/Channel/NoiseModel/$ns3::TcpSocketBase
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::UanNetDevice/Channel/PropagationModel/$ns3::Ipv4L4Protocol/$ns3::TcpL4Protocol/SocketList/[i]
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::UanNetDevice/Channel/PropagationModel/$ns3::TcpL4Protocol/SocketList/[i]
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::UanNetDevice/Channel/PropagationModel/$ns3::TcpSocket/$ns3::TcpSocketBase
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::UanNetDevice/Channel/PropagationModel/$ns3::TcpSocketBase
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::UanNetDevice/Mac/$ns3::Ipv4L4Protocol/$ns3::TcpL4Protocol/SocketList/[i]
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::UanNetDevice/Mac/$ns3::TcpL4Protocol/SocketList/[i]
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::UanNetDevice/Mac/$ns3::TcpSocket/$ns3::TcpSocketBase
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::UanNetDevice/Mac/$ns3::TcpSocketBase
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::UanNetDevice/Phy/$ns3::Ipv4L4Protocol/$ns3::TcpL4Protocol/SocketList/[i]
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::UanNetDevice/Phy/$ns3::TcpL4Protocol/SocketList/[i]
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::UanNetDevice/Phy/$ns3::TcpSocket/$ns3::TcpSocketBase
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::UanNetDevice/Phy/$ns3::TcpSocketBase
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::UanNetDevice/Transducer/$ns3::Ipv4L4Protocol/$ns3::TcpL4Protocol/SocketList/[i]
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::UanNetDevice/Transducer/$ns3::TcpL4Protocol/SocketList/[i]
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::UanNetDevice/Transducer/$ns3::TcpSocket/$ns3::TcpSocketBase
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::UanNetDevice/Transducer/$ns3::TcpSocketBase
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::WimaxNetDevice/$ns3::BaseStationNetDevice/BsIpcsPacketClassifier/$ns3::Ipv4L4Protocol/$ns3::TcpL4Protocol/SocketList/[i]
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::WimaxNetDevice/$ns3::BaseStationNetDevice/BsIpcsPacketClassifier/$ns3::TcpL4Protocol/SocketList/[i]
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::WimaxNetDevice/$ns3::BaseStationNetDevice/BsIpcsPacketClassifier/$ns3::TcpSocket/$ns3::TcpSocketBase
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::WimaxNetDevice/$ns3::BaseStationNetDevice/BsIpcsPacketClassifier/$ns3::TcpSocketBase
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::WimaxNetDevice/$ns3::BaseStationNetDevice/LinkManager/$ns3::Ipv4L4Protocol/$ns3::TcpL4Protocol/SocketList/[i]
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::WimaxNetDevice/$ns3::BaseStationNetDevice/LinkManager/$ns3::TcpL4Protocol/SocketList/[i]
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::WimaxNetDevice/$ns3::BaseStationNetDevice/LinkManager/$ns3::TcpSocket/$ns3::TcpSocketBase
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::WimaxNetDevice/$ns3::BaseStationNetDevice/LinkManager/$ns3::TcpSocketBase
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::WimaxNetDevice/$ns3::BaseStationNetDevice/SSManager/$ns3::Ipv4L4Protocol/$ns3::TcpL4Protocol/SocketList/[i]
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::WimaxNetDevice/$ns3::BaseStationNetDevice/SSManager/$ns3::TcpL4Protocol/SocketList/[i]
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::WimaxNetDevice/$ns3::BaseStationNetDevice/SSManager/$ns3::TcpSocket/$ns3::TcpSocketBase
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::WimaxNetDevice/$ns3::BaseStationNetDevice/SSManager/$ns3::TcpSocketBase
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::WimaxNetDevice/$ns3::BaseStationNetDevice/ServiceFlowManager/$ns3::Ipv4L4Protocol/$ns3::TcpL4Protocol/SocketList/[i]
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::WimaxNetDevice/$ns3::BaseStationNetDevice/ServiceFlowManager/$ns3::TcpL4Protocol/SocketList/[i]
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::WimaxNetDevice/$ns3::BaseStationNetDevice/ServiceFlowManager/$ns3::TcpSocket/$ns3::TcpSocketBase
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::WimaxNetDevice/$ns3::BaseStationNetDevice/ServiceFlowManager/$ns3::TcpSocketBase
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::WimaxNetDevice/$ns3::SubscriberStationNetDevice/Classifier/$ns3::Ipv4L4Protocol/$ns3::TcpL4Protocol/SocketList/[i]
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::WimaxNetDevice/$ns3::SubscriberStationNetDevice/Classifier/$ns3::TcpL4Protocol/SocketList/[i]
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::WimaxNetDevice/$ns3::SubscriberStationNetDevice/Classifier/$ns3::TcpSocket/$ns3::TcpSocketBase
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::WimaxNetDevice/$ns3::SubscriberStationNetDevice/Classifier/$ns3::TcpSocketBase
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::WimaxNetDevice/$ns3::SubscriberStationNetDevice/LinkManager/$ns3::Ipv4L4Protocol/$ns3::TcpL4Protocol/SocketList/[i]
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::WimaxNetDevice/$ns3::SubscriberStationNetDevice/LinkManager/$ns3::TcpL4Protocol/SocketList/[i]
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::WimaxNetDevice/$ns3::SubscriberStationNetDevice/LinkManager/$ns3::TcpSocket/$ns3::TcpSocketBase
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::WimaxNetDevice/$ns3::SubscriberStationNetDevice/LinkManager/$ns3::TcpSocketBase
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::WimaxNetDevice/$ns3::SubscriberStationNetDevice/SSScheduler/$ns3::Ipv4L4Protocol/$ns3::TcpL4Protocol/SocketList/[i]
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::WimaxNetDevice/$ns3::SubscriberStationNetDevice/SSScheduler/$ns3::TcpL4Protocol/SocketList/[i]
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::WimaxNetDevice/$ns3::SubscriberStationNetDevice/SSScheduler/$ns3::TcpSocket/$ns3::TcpSocketBase
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::WimaxNetDevice/$ns3::SubscriberStationNetDevice/SSScheduler/$ns3::TcpSocketBase
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::WimaxNetDevice/BandwidthManager/$ns3::Ipv4L4Protocol/$ns3::TcpL4Protocol/SocketList/[i]
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::WimaxNetDevice/BandwidthManager/$ns3::TcpL4Protocol/SocketList/[i]
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::WimaxNetDevice/BandwidthManager/$ns3::TcpSocket/$ns3::TcpSocketBase
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::WimaxNetDevice/BandwidthManager/$ns3::TcpSocketBase
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::WimaxNetDevice/BurstProfileManager/$ns3::Ipv4L4Protocol/$ns3::TcpL4Protocol/SocketList/[i]
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::WimaxNetDevice/BurstProfileManager/$ns3::TcpL4Protocol/SocketList/[i]
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::WimaxNetDevice/BurstProfileManager/$ns3::TcpSocket/$ns3::TcpSocketBase
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::WimaxNetDevice/BurstProfileManager/$ns3::TcpSocketBase
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::WimaxNetDevice/Channel/$ns3::UanChannel/NoiseModel/$ns3::Ipv4L4Protocol/$ns3::TcpL4Protocol/SocketList/[i]
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::WimaxNetDevice/Channel/$ns3::UanChannel/NoiseModel/$ns3::TcpL4Protocol/SocketList/[i]
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::WimaxNetDevice/Channel/$ns3::UanChannel/NoiseModel/$ns3::TcpSocket/$ns3::TcpSocketBase
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::WimaxNetDevice/Channel/$ns3::UanChannel/NoiseModel/$ns3::TcpSocketBase
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::WimaxNetDevice/Channel/$ns3::UanChannel/PropagationModel/$ns3::Ipv4L4Protocol/$ns3::TcpL4Protocol/SocketList/[i]
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::WimaxNetDevice/Channel/$ns3::UanChannel/PropagationModel/$ns3::TcpL4Protocol/SocketList/[i]
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::WimaxNetDevice/Channel/$ns3::UanChannel/PropagationModel/$ns3::TcpSocket/$ns3::TcpSocketBase
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::WimaxNetDevice/Channel/$ns3::UanChannel/PropagationModel/$ns3::TcpSocketBase
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::WimaxNetDevice/ConnectionManager/$ns3::Ipv4L4Protocol/$ns3::TcpL4Protocol/SocketList/[i]
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::WimaxNetDevice/ConnectionManager/$ns3::TcpL4Protocol/SocketList/[i]
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::WimaxNetDevice/ConnectionManager/$ns3::TcpSocket/$ns3::TcpSocketBase
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::WimaxNetDevice/ConnectionManager/$ns3::TcpSocketBase
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::WimaxNetDevice/Phy/Channel/$ns3::UanChannel/NoiseModel/$ns3::Ipv4L4Protocol/$ns3::TcpL4Protocol/SocketList/[i]
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::WimaxNetDevice/Phy/Channel/$ns3::UanChannel/NoiseModel/$ns3::TcpL4Protocol/SocketList/[i]
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::WimaxNetDevice/Phy/Channel/$ns3::UanChannel/NoiseModel/$ns3::TcpSocket/$ns3::TcpSocketBase
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::WimaxNetDevice/Phy/Channel/$ns3::UanChannel/NoiseModel/$ns3::TcpSocketBase
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::WimaxNetDevice/Phy/Channel/$ns3::UanChannel/PropagationModel/$ns3::Ipv4L4Protocol/$ns3::TcpL4Protocol/SocketList/[i]
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::WimaxNetDevice/Phy/Channel/$ns3::UanChannel/PropagationModel/$ns3::TcpL4Protocol/SocketList/[i]
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::WimaxNetDevice/Phy/Channel/$ns3::UanChannel/PropagationModel/$ns3::TcpSocket/$ns3::TcpSocketBase
- /NodeList/[i]/DeviceList/[i]/$ns3::WimaxNetDevice/Phy/Channel/$ns3::UanChannel/PropagationModel/$ns3::TcpSocketBase
No Attributes defined for this type.
Attributes defined in parent class ns3::TcpSocket:
-
SndBufSize: TcpSocket maximum transmit buffer size (bytes)
- Set with class: ns3::UintegerValue
- Underlying type: uint32_t 0:4294967295
- Initial value: 131072
- Flags: construct write read
-
RcvBufSize: TcpSocket maximum receive buffer size (bytes)
- Set with class: ns3::UintegerValue
- Underlying type: uint32_t 0:4294967295
- Initial value: 131072
- Flags: construct write read
-
SegmentSize: TCP maximum segment size in bytes (may be adjusted based on MTU discovery)
- Set with class: ns3::UintegerValue
- Underlying type: uint32_t 0:4294967295
- Initial value: 536
- Flags: construct write read
-
SlowStartThreshold: TCP slow start threshold (bytes)
- Set with class: ns3::UintegerValue
- Underlying type: uint32_t 0:4294967295
- Initial value: 65535
- Flags: construct write read
-
InitialCwnd: TCP initial congestion window size (segments)
- Set with class: ns3::UintegerValue
- Underlying type: uint32_t 0:4294967295
- Initial value: 1
- Flags: construct write read
- ConnTimeout: TCP retransmission timeout when opening connection (seconds)
-
ConnCount: Number of connection attempts (SYN retransmissions) before returning failure
- Set with class: ns3::UintegerValue
- Underlying type: uint32_t 0:4294967295
- Initial value: 6
- Flags: construct write read
- DelAckTimeout: Timeout value for TCP delayed acks, in seconds
-
DelAckCount: Number of packets to wait before sending a TCP ack
- Set with class: ns3::UintegerValue
- Underlying type: uint32_t 0:4294967295
- Initial value: 2
- Flags: construct write read
- PersistTimeout: Persist timeout to probe for rx window
TraceSources defined for this type:
- RTO: Retransmission timeout
- RTT: Last RTT sample
- NextTxSequence: Next sequence number to send (SND.NXT)
- HighestSequence: Highest sequence number ever sent in socket's life time
- State: TCP state
- RWND: Remote side's flow control window
Reimplemented from ns3::TcpSocket.
Reimplemented in ns3::TcpNewReno, ns3::TcpReno, ns3::TcpRfc793, and ns3::TcpTahoe.
| virtual int ns3::TcpSocketBase::Listen | ( | void | ) | [virtual] |
Listen for incoming connections.
- Returns:
- 0 on success, -1 on error (in which case errno is set).
Implements ns3::Socket.
Reimplemented in ns3::TcpNewReno, ns3::TcpReno, and ns3::TcpTahoe.
Read data from the socket.
This function matches closely in semantics to the recv() function call in the standard C library (libc): ssize_t recv (int s, void *buf, size_t len, int flags); except that the receive I/O is asynchronous. This is the primary Recv method at this low-level API and must be implemented by subclasses.
This method is normally used only on a connected socket. In a typical blocking sockets model, this call would block until at least one byte is returned or the connection closes. In ns-3 at this API, the call returns immediately in such a case and returns 0 if nothing is available to be read. However, an application can set a callback, ns3::SetRecvCallback, to be notified of data being available to be read (when it conceptually unblocks); this is an asynchronous I/O model for recv().
This variant of Recv() uses class ns3::Packet to encapsulate data, rather than providing a raw pointer and length field. This allows an ns-3 application to attach tags if desired (such as a flow ID) and may allow the simulator to avoid some data copies. Despite the appearance of receiving Packets on a stream socket, just think of it as a fancy byte buffer with streaming semantics.
The semantics depend on the type of socket. For a datagram socket, each Recv() returns the data from at most one Send(), and order is not necessarily preserved. For a stream socket, the bytes are delivered in order, and on-the-wire packet boundaries are not preserved.
The flags argument is formed by or'ing one or more of the values: MSG_OOB process out-of-band data MSG_PEEK peek at incoming message None of these flags are supported for now.
Some variants of Recv() are supported as additional API, including RecvFrom(), overloaded Recv() without arguments, and variants that use raw character buffers.
- Parameters:
-
maxSize reader will accept packet up to maxSize flags Socket control flags
- Returns:
- Ptr<Packet> of the next in-sequence packet. Returns 0 if the socket cannot return a next in-sequence packet conforming to the maxSize and flags.
- See also:
- SetRecvCallback
Implements ns3::Socket.
| virtual Ptr<Packet> ns3::TcpSocketBase::RecvFrom | ( | uint32_t | maxSize, | |
| uint32_t | flags, | |||
| Address & | fromAddress | |||
| ) | [virtual] |
Read a single packet from the socket and retrieve the sender address.
Calls Recv(maxSize, flags) with maxSize implicitly set to maximum sized integer, and flags set to zero.
This method has similar semantics to Recv () but subclasses may want to provide checks on socket state, so the implementation is pushed to subclasses.
- Parameters:
-
maxSize reader will accept packet up to maxSize flags Socket control flags fromAddress output parameter that will return the address of the sender of the received packet, if any. Remains untouched if no packet is received.
- Returns:
- Ptr<Packet> of the next in-sequence packet. Returns 0 if the socket cannot return a next in-sequence packet.
Implements ns3::Socket.
Send data (or dummy data) to the remote host.
This function matches closely in semantics to the send() function call in the standard C library (libc): ssize_t send (int s, const void *msg, size_t len, int flags); except that the send I/O is asynchronous. This is the primary Send method at this low-level API and must be implemented by subclasses.
In a typical blocking sockets model, this call would block upon lack of space to hold the message to be sent. In ns-3 at this API, the call returns immediately in such a case, but the callback registered with SetSendCallback() is invoked when the socket has space (when it conceptually unblocks); this is an asynchronous I/O model for send().
This variant of Send() uses class ns3::Packet to encapsulate data, rather than providing a raw pointer and length field. This allows an ns-3 application to attach tags if desired (such as a flow ID) and may allow the simulator to avoid some data copies. Despite the appearance of sending Packets on a stream socket, just think of it as a fancy byte buffer with streaming semantics.
If either the message buffer within the Packet is too long to pass atomically through the underlying protocol (for datagram sockets), or the message buffer cannot entirely fit in the transmit buffer (for stream sockets), -1 is returned and SocketErrno is set to ERROR_MSGSIZE. If the packet does not fit, the caller can split the Packet (based on information obtained from GetTxAvailable) and reattempt to send the data.
The flags argument is formed by or'ing one or more of the values: MSG_OOB process out-of-band data MSG_DONTROUTE bypass routing, use direct interface These flags are _unsupported_ as of ns-3.1.
- Parameters:
-
p ns3::Packet to send flags Socket control flags
- Returns:
- the number of bytes accepted for transmission if no error occurs, and -1 otherwise.
- See also:
- SetSendCallback
Implements ns3::Socket.
| virtual int ns3::TcpSocketBase::SendTo | ( | Ptr< Packet > | p, | |
| uint32_t | flags, | |||
| const Address & | toAddress | |||
| ) | [virtual] |
Send data to a specified peer.
This method has similar semantics to Send () but subclasses may want to provide checks on socket state, so the implementation is pushed to subclasses.
- Returns:
- -1 in case of error or the number of bytes copied in the internal buffer and accepted for transmission.
Implements ns3::Socket.
| virtual bool ns3::TcpSocketBase::SetAllowBroadcast | ( | bool | allowBroadcast | ) | [protected, virtual] |
Configure whether broadcast datagram transmissions are allowed.
This method corresponds to using setsockopt() SO_BROADCAST of real network or BSD sockets. If set on a socket, this option will enable or disable packets to be transmitted to broadcast destination addresses.
- Parameters:
-
allowBroadcast Whether broadcast is allowed
- Returns:
- true if operation succeeds
Implements ns3::Socket.
| virtual int ns3::TcpSocketBase::ShutdownRecv | ( | void | ) | [virtual] |
- Returns:
- zero on success, -1 on failure.
Do not allow any further Recv calls. This method is typically implemented for Tcp sockets by a half close.
Implements ns3::Socket.
| virtual int ns3::TcpSocketBase::ShutdownSend | ( | void | ) | [virtual] |
- Returns:
- zero on success, -1 on failure.
Do not allow any further Send calls. This method is typically implemented for Tcp sockets by a half close.
Implements ns3::Socket.
The documentation for this class was generated from the following files:
- src/internet-stack/tcp-socket-base.h
- doc/introspected-doxygen.h
 1.6.1
1.6.1